This post may contain affiliate links at no additional cost to you. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Click to view our full disclosure.
What's inside
Welcome to my breakdown of the best foods to gain muscle.
If you are truly serious about your goals, you need a more strategic approach, including food choices you make. As a pro trainer, I remind my clients of this all of the time.
To go a step further, I’ve dug deep in the world of bodybuilders, athletes, and film stars. I know how their diets contributed to some jaw-dropping body transformations.
And now, I’m here to share the ultimate 20 muscle-building foods list with you.
Keep reading and prepare your taste buds for a mouth-watering experience fueling you to muscle greatness!
What is the importance of eating the right foods?
Related: Best 12 Week Carb Cycling Meal Plan For Fat Loss (With PDF)
Eating the right food serves a wider purpose than just helping you build an incredible head-turning physique. While it’s certainly good for that, too, eating the right food sources can aid in:
Better athletic performance

Energy imbalance happens when you train a lot and don’t eat enough. This can result in reduced performance, overtraining, and burnout.
Fueling your body with nutritious, mineral and vitamin-rich food can increase your energy and improve your performance.
Also, different macros play different roles in our bodies. Eating protein-rich food increases muscle growth and muscle repair.
Adequate carbohydrates intake from the right food sources can restore glycogen and recondition the muscles. Fats regulate hormones and reduce inflammation.
Getting these macros from the right food sources like whole grains, nuts, fish, lean meat, beans, lentils, fruit, and vegetables is essential!
| PRO TIPS: Aim for 0.6-1 grams/ pound of body weight for protein and 2.5 -4 grams/pound of body weight for carbs. Get at least 20% of your daily calorie intake from fat. This can be ideal for strength training and endurance events to improve performance. You can also use our special and advanced calorie and macro calculator for a more precise recommendation for muscle growth or maintenance. |
Speed up your recovery
The right foods will restore muscle condition and repair damaged tissue. A good diet can speed up recovery not just after training, but during and after illnesses, too.
Consume appropriate amounts of energy, nutrients, and fluids. Align your diet with your training schedules to maximize your performance, prevent injuries, or recover quicker!
Prevent atrophy (muscle loss)
We know that a high-protein diet can help build muscles and repair the tissue after training. What you may not know is that it can slow down or prevent muscle loss, too.
Muscle loss can happen after long immobilization, which is essential in cases like fractures and other injuries. Eating healthy while you are recovering from an injury therefore can slow down muscle loss, even during immobilization.
It may also come as a surprise that bad nutrition and overtraining can lead to muscle atrophy!
That’s because the wrong food choices and overtraining leads to imbalances in hormone levels. For instance, you may experience reduced testosterone and an increase in cortisol, leading to muscle loss, illnesses, and even weight gain.
Metabolic health

The right food sources have pre and probiotics that keep the gut healthy. It also reduces inflammation, regulates your blood sugar and cholesterol, and may improve your metabolic health.
Higher basal metabolic rate (you burn more calories while resting)
BMR is the energy your body needs for maintaining function, including breathing, digestion, blood flow etc.
The more muscles you have, the more calories you burn. But to have more muscles, you need to eat the right food, as it requires a lot of energy to maintain it.
Therefore, training with good nutrition will increase your muscle mass, resulting in a higher basal metabolic rate. This can also help with fat and weight loss.
Cardiovascular health
All this said above, the importance of eating the right food is to prevent obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol, which can all lead to cardiovascular disease.
How does nutrition impact muscle gain?
Your muscles sustain damage (stimulus) while training to grow. This is called hypertrophy. But the food that you eat throughout the day is what repairs these damaged muscle fibers and stimulates them to grow bigger and stronger.
In particular, protein is what provides the building blocks of amino acids to activate muscle synthesis (muscle remodeling), making it the main muscle-building and maintenance source.
This doesn’t mean carbs and fat aren’t important. They all work together to provide you with the right amount of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Every piece plays a role in building muscle, repairing tissue, and regulating your hormones.
20 Best Muscle-Building Foods
1. Chicken Breast

Benefits
Chicken is the number-one bodybuilding food! It contains a high amount of protein and is low in fat and carbs and calories, with 100g of chicken having only 165 Kcals. This is good for weight loss, too.
It is rich in vitamin B6, which is important for energy metabolism, brain function, and red blood cell formation. It contains selenium, which acts as a powerful antioxidant and supports thyroid and immune function.
Preparation ideas:
Grill whole or parts, add it to stir frys, give it a coating, poach, or boil. You can get as creative as you like when it comes to chicken.
Flavor it sweet with honey and mustard or korma if you have a sweet tooth, or go spicy in a curry or pan-fried style.
Possible downsides:
While it has numerous health benefits, people with kidney problems or chronic heart disease should consume chicken in moderation.
That’s because high-protein foods like chicken make your kidneys work harder.
Safety considerations:
Undercooked, out of date, slimy, discolored chicken can cause food poisoning and salmonella. Make sure your chicken is in the fridge or freezer and always check expiration dates. Cook thoroughly; chicken should never be pink inside.
2. Eggs

Benefits
Eggs are a nutrient powerhouse, providing high-quality protein that contains all essential amino acids crucial for muscle growth and repair.
They are also abundant in vitamins B12, D, and E, as well as minerals like zinc and iron, which play a vital role in supporting overall muscle development and function.
Preparation ideas:
Begin your day with a protein-packed breakfast by trying out various egg preparations like scrambled eggs with a medley of vegetables or a flavorful vegetable omelet.
Possible downsides:
While eggs are a nutritious choice, it’s important to note that some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to eggs. While eggs are classified as Additionally, excessive consumption of eggs may lead to elevated cholesterol levels in some people.
I would like to highlight the word ‘excessive’, as most cholesterol increase is due to saturated and trans fats (deep fried food, cream, processed meat). Eggs are considered unsaturated fats, with only 3.4 grams being saturated.
According to AHA, people with high cholesterol can still eat up to 6 eggs per week or just simply remove the yolk!
Safety Considerations:
To reduce the risk of salmonella contamination, it’s crucial to handle and cook eggs properly. Keep them refrigerated and cook them until the yolks and whites are firm.
3. Greek Yogurt

Benefits:
Greek yogurt is an excellent source of protein, delivering both whey and casein proteins that are essential for muscle recovery and growth.
Additionally, it contains probiotics that promote healthy digestion, aiding in nutrient absorption and supporting optimal muscle repair.
Preparation ideas:
Enjoy Greek yogurt with fresh fruits and a drizzle of honey for a nutritious and creamy snack.
Possible downsides:
Greek yogurt may not be suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies.
Safety considerations:
Ensure that Greek yogurt is stored at appropriate temperatures to prevent bacterial growth and foodborne illnesses.
4. Lean Beef

Benefits:
Lean beef is a protein and creatine powerhouse, supplying essential amino acids necessary for muscle synthesis and repair.
It is also a rich source of iron and zinc, two minerals crucial for oxygen transport and hormone regulation, supporting muscle function and development.
Preparation ideas:
Grill or broil lean beef steaks or make homemade beef burgers using lean ground beef.
Possible downsides:
High consumption of red meat, including lean beef, has been associated with certain health risks such as heart disease and colon cancer.
Safety considerations:
Practice safe handling and cooking of beef to prevent bacterial contamination and ensure it reaches the appropriate internal temperature.
5. Tuna

Benefits:
Tuna is a lean protein source, providing both protein and omega-3 fatty acids. The omega-3 fatty acids in tuna possess anti-inflammatory properties, aiding in muscle recovery, while the protein content supports muscle growth and repair.
Furthermore, tuna is a good source of vitamin D, which contributes to muscle function and overall health.
Preparation ideas:
Make a refreshing tuna salad with chopped vegetables and light dressing or enjoy grilled tuna steaks.
Possible downsides:
Tuna, especially certain species like bluefin tuna, may contain high levels of mercury, which can be harmful if consumed in large quantities.
According to the FDA, people can still consume 2-3 portions per week safely!
Safety considerations:
Choose fresh or properly stored tuna to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
6. Quinoa

Benefits:
Quinoa is a plant-based complete protein, containing all essential amino acids required for muscle growth and repair.
It is also a complex carbohydrate source, providing sustained energy for workouts and assisting in muscle glycogen replenishment.
Preparation ideas:
Cook quinoa as a base for grain bowls or mix it with vegetables and herbs for a flavorful side dish.
Possible downsides:
Quinoa is generally safe to consume, but in rare cases, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction.
Safety considerations:
Thoroughly rinse quinoa before cooking to remove the bitter-tasting saponins on its surface.
7. Cottage Cheese

Benefits:
Cottage cheese is an excellent source of casein protein, which is slow-digesting and releases amino acids gradually, supporting overnight muscle recovery.
It is also rich in calcium, an important mineral for muscle contractions and overall bone health.
Preparation ideas:
Top cottage cheese with fruits or use it as a creamy filling for wraps and sandwiches.
Possible downsides:
Cottage cheese is high in sodium, so individuals on a low-sodium diet should consume it in moderation.
Safety considerations:
Keep cottage cheese refrigerated and discard any spoiled or expired products.
8. Sweet Potatoes

Benefits:
Sweet potatoes are a valuable source of complex carbohydrates, supplying steady energy for intense workouts and aiding in replenishing muscle glycogen stores.
They are also packed with vitamins A and C, as well as potassium, supporting muscle function and reducing the likelihood of cramping.
Preparation ideas:
Bake or roast sweet potatoes and enjoy them as a side dish or stuffed with your favorite fillings.
Possible downsides:
While sweet potatoes are healthy, consuming them in large quantities may contribute to an excessive intake of carbohydrates.
Safety considerations:
Store sweet potatoes in a cool, dark place to prevent sprouting or spoilage.
9. Almonds

Benefits:
Almonds are a nutritious source of monounsaturated fats, which help maintain optimal hormone levels, promoting muscle growth and development.
They are also rich in vitamin E, acting as an antioxidant and supporting muscle recovery.
Preparation ideas:
Snack on raw almonds or sprinkle them over salads and stir-fries for added crunch and nutrition.
Possible downsides:
Almonds are high in calories, so individuals watching their calorie intake should be mindful of portion sizes.
Safety considerations:
Store almonds in an airtight container in a cool, dry place to maintain freshness and prevent infestation.
10. Broccoli

Benefits
Broccoli is a nutrient-dense vegetable, providing antioxidants and phytochemicals that combat inflammation and oxidative stress, promoting muscle recovery and growth.
It is also an excellent source of vitamin C, contributing to collagen production and supporting muscle and connective tissue health.
Preparation ideas:
Steam or roast broccoli florets and serve them as a side or add them to stir-fries and pasta dishes.
Possible downsides:
Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort or gas when consuming broccoli raw or in large amounts.
Safety considerations:
Wash broccoli thoroughly and remove any damaged or discolored parts before cooking.
11. Salmon
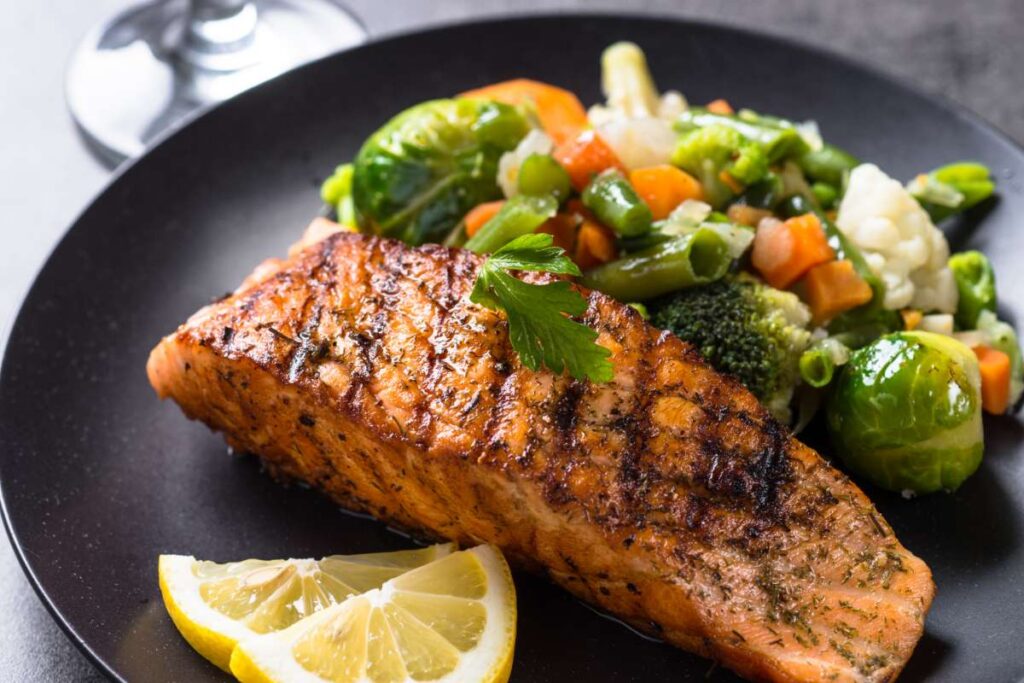
Benefits:
Salmon is a fatty fish abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which aid in muscle recovery and growth.
It is also a rich source of high-quality protein and vitamin D, both important for muscle health and function.
Preparation ideas:
Grill or bake salmon fillets with herbs and lemon for a delicious and omega-3-rich meal.
Possible downsides:
Salmon may contain environmental pollutants such as mercury and PCBs, so it’s important to choose wild-caught or responsibly farmed varieties.
Safety considerations:
Ensure that salmon is properly stored and cooked to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination.
12. Brown Rice

Benefits:
Brown rice is a complex carbohydrate source, providing sustained energy for workouts and assisting in muscle glycogen replenishment.
It is also high in fiber, promoting healthy digestion and helping maintain stable blood sugar levels for optimal energy and muscle growth.
Preparation ideas:
Cook brown rice as a nutritious alternative to white rice and use it as a base for stir-fries and grain bowls.
Possible downsides:
Brown rice contains phytic acid, which can hinder the absorption of certain minerals. Soaking or fermenting brown rice can help reduce this effect.
Safety considerations:
Store brown rice in airtight containers to prevent moisture and insect infestation.
13. Lentils

Benefits:
Lentils offer a balanced combination of protein and complex carbohydrates, delivering nutrients necessary for muscle recovery and growth. They are also rich in iron and folate, supporting oxygen transport and red blood cell production, crucial for muscle performance.
Preparation ideas:
Prepare lentil soups, stews, or curries, or use them in salads and veggie burgers for a protein boost.
Possible downsides:
Lentils can cause bloating or digestive issues in some individuals, especially if not cooked properly.
Safety considerations:
Purchase lentils from reputable sources and store them in a cool, dry place to maintain freshness and prevent rancidity.
14. Spinach

Benefits:
Spinach is a nutrient-rich leafy green, providing vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote muscle health, including iron, magnesium, and vitamin K.
Its nitrate content helps enhance blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles, improving performance and recovery.
Preparation ideas:
Enjoy fresh spinach in salads or sauté it with garlic and olive oil as a nutritious side dish.
Possible downsides:
Spinach contains oxalates, which can contribute to kidney stone formation in susceptible individuals. Cooking spinach can help reduce oxalate levels.
Safety Considerations:
Wash spinach thoroughly to remove dirt and potential contaminants before consuming.
15. Beef Liver

Benefits:
Beef liver is nutrient-dense organ meat, providing high-quality protein and essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth and repair.
It is particularly rich in vitamin A, vitamin B12, iron, and zinc, all crucial for muscle function and development.
Preparation ideas:
Cook beef liver with onions and spices for a nutrient-dense and flavorful main course.
Possible downsides:
Beef liver is high in cholesterol and should be consumed in moderation, especially by individuals with high cholesterol levels.
Safety considerations:
Choose high-quality beef liver from trusted sources and cook it to a safe internal temperature.
16. Turkey Breast

Benefits:
Turkey breast is a lean protein source, supporting muscle repair and growth without excessive fat intake.
It is also rich in vitamin B6 and niacin, which aid energy production and regulate muscle protein synthesis.
Preparation ideas:
Roast or grill turkey breast slices and use them in sandwiches, wraps, or salads.
Possible downsides:
Processed turkey breast products, such as deli meats, may contain additives and high sodium content. Choosing minimally processed options is recommended.
Safety Considerations:
Cook turkey breast to the recommended internal temperature to eliminate any harmful bacteria.
17. Oats

Benefits:
Oats are a whole grain carbohydrate source, providing sustained energy for workouts and aiding in muscle recovery.
They are also high in fiber, promoting healthy digestion and helping maintain stable blood sugar levels for optimal muscle growth.
Preparation ideas:
Start your day with a hearty bowl of oatmeal topped with fruits, nuts, and a drizzle of maple syrup.
Possible downsides:
While oats are generally safe, and are gluten-free, some oats might contain gluten if they were processed in a plant that also handles gluten products! That’s why it’s important for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance to opt for certified gluten-free oats.
Safety considerations:
Purchase oats from reputable sources and store them in a dry place to prevent moisture and insect contamination.
18. Milk

Benefits:
Milk contains a combination of whey and casein proteins, supplying fast and slow-release amino acids for muscle repair and growth.
It is also a good source of calcium and vitamin D, essential for muscle contractions, bone health, and overall muscle function.
Preparation ideas:
Use milk as a base for smoothies, enjoy it with cereal, or add it to recipes for creamy sauces and soups.
Possible downsides:
Some individuals may be lactose intolerant or have dairy allergies, in which case alternative milk options should be considered.
Safety considerations:
Store milk at appropriate temperatures and check for signs of spoilage before consuming.
19. Chickpeas

Benefits:
Chickpeas offer a balanced combination of protein and complex carbohydrates, supporting muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment. They are also high in fiber, promoting healthy digestion and helping maintain stable blood sugar levels for optimal muscle growth.
Preparation ideas:
Roast chickpeas for a crunchy snack or use them in salads, soups, and curries for added protein and fiber.
Possible downsides:
Chickpeas may cause gas or digestive discomfort in some individuals, particularly if not cooked thoroughly.
Safety Considerations:
Soak and cook chickpeas thoroughly to ensure they are safe to consume.
20. Pumpkin Seeds

Benefits:
Pumpkin seeds are a nutritious source of plant-based protein and healthy fats, contributing to muscle repair and providing energy.
They are rich in minerals like magnesium and zinc, supporting muscle function, protein synthesis, and recovery.
Preparation ideas:
Sprinkle pumpkin seeds over salads or roast them for a crunchy and nutritious snack.
Possible downsides:
Individuals with nut allergies may also be allergic to pumpkin seeds, as they belong to the same botanical family.
Safety considerations:
Purchase pumpkin seeds from reputable sources and store them in a cool, dry place to maintain freshness and prevent rancidity.
Foods To Avoid When Building Muscle and Why
I believe in balance, so treat these as “cheat meals” and consume them in moderation!
Processed Foods
Processed food comes with high calorie content, sugar, and unhealthy fat. Also, they don’t keep you full for long (fast release meals), resulting in overeating which can contribute to weight gain.
Chocolate, sodas, chips, ice cream, pasties, pastries, and many canned foods are all good examples of processed food. Be sensible as consuming high amounts of processed food can seriously harm your health.
Sugary Drinks
Sugary drinks can increase your blood sugar level suddenly, leading to an energy crash, which isn’t ideal for performance.
The sudden increase in blood sugar can also store energy as fat! Sugary drinks are also not ideal for hydration as they often contain high amounts of sugar, artificial additives, and caffeine.
High-Fat Foods
High-fat foods are packed with calories and can lead to weight gain if consumed excessively.
Unhealthy fats (trans fats) like pizza, burgers, chips, and ice cream are especially harmful to our health. Eating them can lead to heart disease by increasing bad cholesterol. It can also decrease nutrient absorption, like omega 3 fatty acids.
Conversely, healthy fats like fish, avocado, nuts, and seeds can regulate hormone levels and speed up recovery while also keeping our heart healthy. Although they are high in calories, I still recommend adding them.
Alcohol
Alcohol consumption can interfere with muscle recovery and protein synthesis. It can also negatively impact hormonal balance and dehydrate the body, all of which can hinder muscle growth and recovery.
Fast Food
You never really know what comes in a package. Is it real food?
I wouldn’t call it that! These are often packed with trans fats, refined sugar, palm oil or other low-quality ingredients, which is why it’s cheap and fast.
Fast foods lack essential nutrients and generally have very little nutritional value. Eating them can lead to weight gain and poor health on top of hindering your muscle-building goals.
Added Sugars
Sugary drinks, cakes, and desserts are empty calories without nutritional value. Excessive sugar intake can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, inflammation, and impaired muscle growth.
Fried Foods
Fried foods are high in trans fats and have no nutritional value. They are also high in calories and lead to weight gain.
Best 7 Day Meal Plan for Muscle Gain
Ready to build muscle with all of the right foods? Here’s a weeklong meal plan to get you started.
Please note that the quantity of food mentioned in this diet plan varies based on factors such as weight, height, age, activity levels, and specific goals.
Individual needs may differ, and this plan does not and should not replace professional help. The following plan is merely a general example of a diet plan designed to promote muscle gain.
Monday:
| Breakfast | Peanut Butter on Toast 2 slices whole grain bread + 2 tbsp peanut butter + 1 medium banana |
| Snack | 1 sugar free protein bar |
| Lunch | Teriyaki Chicken with Brown Rice6 oz chicken breast + ½ cup teriyaki sauce + 1 cup cooked brown rice |
| Afternoon Snack | 1 cup Greek Yogurt with Granola |
| Dinner | Salmon Fillet with Sweet Potato and Asparagus 6 oz salmon fillet + 1 medium sweet potato + 1 cup asparagus |
| Bedtime Snack | Cottage Cheese with Berries ½ cup cottage cheese + 1/2 cup mixed berries |
Tuesday
| Breakfast | Scrambled Eggs with Avocado 3 eggs + 1/2 avocado |
| Snack | 1 cup Greek Yogurt with Berries |
| Lunch | Salmon Teriyaki with Quinoa 6 oz salmon fillet + 1 cup cooked quinoa |
| Afternoon Snack | Whey Protein Shake with Plant Based Milk or Water 1 scoop |
| Dinner | Grilled Chicken Breast with Brown Rice 6 oz chicken breast + 1 cup cooked brown rice |
| Bedtime Snack | Cottage Cheese with Almonds ½ cup cottage cheese + 1 oz almonds |
Wednesday
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with Berries and Honey 1 cup Oatmeal 100 g Berries 1 Tsp Honey |
| Snack | 1 Handful Mixed Nuts |
| Lunch | Stir-Fried Beef and Veggies 4 oz beef + 1 cup mixed vegetables |
| Afternoon Snack | Hummus with Carrot Sticks 2 tbsp hummus + 1 carrot |
| Dinner | 4 oz Tandoori Chicken with Salad As much salad as you like |
| Bedtime Snack | Casein Protein 1 Scoop |
Thursday
| Breakfast | Vegetable Omelet 2 eggs |
| Snack | Rice Cakes with Peanut Butter 2 Rice Cakes with 2 Tbsp of Peanut Butter |
| Lunch | 4 oz Grilled Turkey Breast |
| Afternoon Snack | 1 cup Fruit Salad |
| Dinner | Lentil Curry with Brown Rice 1 cup lentils + 1/2 cup brown rice |
| Bedtime Snack | Greek Yogurt 1 cup |
Friday
| Breakfast | Whole Grain Toast with Avocado and 1 Glass Fresh Fruit Smoothie 3 slices bread + 1 avocado |
| Snack | 1 Cup Greek Yogurt |
| Lunch | Baked Cod with Quinoa 6 oz fish |
| Afternoon Snack | 1 Protein Bar |
| Dinner | 4 oz Thai Basil Chicken |
| Bedtime Snack | ½ Cup Cottage Cheese |
Saturday
| Breakfast | Vegetable Omelet 3 Eggs |
| Snack | 1 Scoop Whey Protein Shake with Plant Based Milk or Water |
| Lunch | Chicken Stir-Fry with Brown Rice 6 oz chicken breast + 1 cup mixed vegetables + 1/2 cup cooked brown rice |
| Afternoon Snack | Greek Yogurt with Nuts 1 cup |
| Dinner | Beef Stir-Fry with Quinoa 6 oz beef strips + 1 cup mixed vegetables + 1/2 cup cooked quinoa |
| Bedtime Snack | 1 Scoop Casein Protein Shake |
Sunday
| Breakfast | 3 Scrambled Eggs |
| Snack | 1 Cup Greek Yogurt |
| Lunch | 6 oz Salmon Teriyaki |
| Afternoon Snack | 1 Scoop Whey Protein Shake with Plant Based Milk or Water |
| Dinner | 4 oz Grilled Chicken Breast |
| Bedtime Snack | ½ cup Cottage Cheese |
Additional Tips for Gaining Muscle Effectively
So much goes into building muscle. I would like you to get the most out of the information I’m sharing, so here are some additional tips for gaining muscle mass effectively!
Focus on Compound Exercises
Compound exercises work multiple muscles (multi-joint) at the same time, allowing you to lift heavier weights. This applies adequate stimulus, challenge on your body and muscles increasing strength, power and muscle growth!
That’s because when you lift you release hormones that are essential for muscle growth and repair, like human growth hormone and testosterone (anabolic hormones).
To get the most out of your training session, you should also gradually increase the weights (progressive overload), as your body adapts quickly to a certain load and stops growing.
So, make sure you leave your comfort zone!
Compound exercises may also be suitable for those lacking time, as you won’t need a two-hour long strength training routine to achieve the same amount of stimulus that you do with compound work.
Lift Heavy Weights with Proper Form
While I’ve highlighted the importance of lifting heavy weight progressively, proper form will be just as important.
Without maintaining correct technique you will get injured and won’t be able to lift at all. So put your ego aside, and lift safely and effectively.
When you lift incorrectly some muscle may also need to compensate, so you will reduce the potential of muscle gain with that exercise.
Prioritize Recovery and Rest Days
Rest days allow your muscles to recondition, recover, grow and refuel! If you don’t give enough time for it to do so, it won’t grow at all or much slower. Insufficient recovery will not only hinder your progress, but reduce your performance and eventually make you ill.
Listen to your body and have some rest days whenever you feel it is needed. I would recommend two recovery days with one being active, including walking or gentle yoga.
You should also sleep seven to nine hours a night, as growth hormone is the highest while sleeping and that can also help build muscle.
Follow a High-Protein Diet
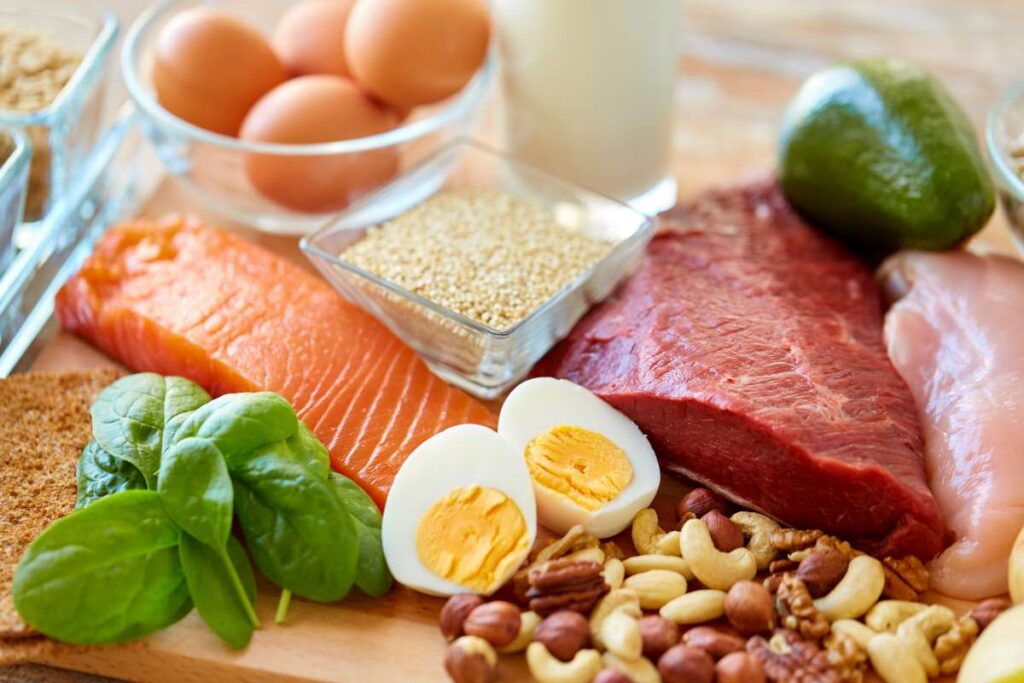

When you eat protein it breaks down into amino acids that are responsible for building muscles (building blocks of protein) and transporting nutrients in our body.
For strength training, it is recommended to consume an even higher amount of protein intake like 1g/pounds of body weight to gain maximum strength and muscle size.
Consume Enough Calories
Muscle mass is expensive. If it costs a lot of calories for your body to maintain it, then imagine how much it costs to grow it.
If maintenance requires that your calories out be equal to your calories in, to build it you need a higher calorie intake.
Of course, so you don’t gain it in the form of fat, choose sensible food sources and high-protein healthy meals.
Incorporate Cardiovascular Exercise

Now that we’ve spoken about fat and muscle gain, the importance of cardio sessions comes into the picture.
Cardio or HIIT can burn extra calories and excess fat, especially when done after weight training.
That’s because your body uses glycogen as energy when lifting. When you run out of glycogen and you do HIIT for 10-15 minutes at the end of your workout, your body will need to reach your fat stores.
Therefore, cardio can be a good addition to your muscle-building training routine.
Although, if you are skinny, I would keep cardio at a minimum. Read more about this in my article on going From Skinny to Buff!
Stay Hydrated
Water plays a crucial role in supporting muscle growth. It helps with hydration, transporting nutrients, protein synthesis, joint health, and temperature regulation during exercise.
Staying properly hydrated is also important for athletic performance and recovery.
Consistency is Key
You need to make healthy eating your priority and lifestyle. That can only be done through consistency and by preparing your food the way you like.
Sticking to the right diet is easier when you know how to flavor it to your tastes – sweet, sour, spicy, hot. Some people naturally have that sweet tooth, and there’s nothing wrong with that.
Consistency will come with joy, you just need to find your way of enjoying healthy food!
Consider Supplements

Supplements can be a great addition to your diet, especially if you are struggling to eat the right amount of macros, like protein. In this case, you can use protein powder to increase your daily protein intake. Not to replace REAL food, but to supplement it!
Meeting your macronutrients daily will always speed up your progress.
Track Your Progress
Where are you starting and where are you heading to? You need to have a destination. Once you reach it, then you set a new one.
I suggest you take pictures before and after monthly, so you can recognize what you have achieved. You can also do body measurements to track your progress.
Conclusion
The right foods to gain muscle are all about boosting strength and boosting performance.
Foods like chicken breast, lentils, nuts, broccoli, and many others are all great sources of nutrients, protein, minerals and vitamins. They all support muscle repair, growth, and overall health!
Incorporating these foods into your lifestyle will maximize your muscle gains, enhance your performance, and make you a health powerhouse!
If you are planning to try these meals or follow our 7-day meal plan, we’d love to hear your feedback!
Frequently Asked Questions
What foods build muscles fast?
Some high-quality, protein-rich, muscle-building foods include white fish, tuna, seafood, lean meat like chicken, turkey, beef, eggs, soybeans, and lentils.
How should I eat to gain muscle?
You should eat five to six smaller meals throughout the day with the aim of 1g/ pounds body weight protein intake.
Research shows that distribution of protein intake evenly throughout the day (breakfast, lunch, dinner, snacks) positively impacts muscle protein synthesis resulting in faster and bigger muscle growth.
When should I eat to gain muscle?
While I can’t give specific time for your busy schedule, I can indeed say eating every two to three hours throughout the day is the best way to build muscle.
Spreading out your protein intake in each meal also results in an increase in muscle mass.
I also advise to have a protein shake one to two hours before training and protein and carb-rich food after to restore muscle condition and recover quicker.
What are the best foods to eat to gain muscle?
High protein food, complex carbs, and healthy fats are the best food to eat for muscle gain.
They fuel your body with nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that are essential for gaining muscle. Some of these food sources include:
High protein: Chicken, turkey, white fish, tuna, eggs
Complex carbs: Oats, lentils, quinoa, couscous
Healthy fat: Oily fish, nuts, seeds, salmon, avocados
Additionally, you should eat a good amount of fruits and vegetables.
How much protein do I need to eat to build muscle?
It is recommended to eat between 0.8-1g/ pound of body weight of protein to gain muscle. This may increase to 1.2 for those with high metabolism and a skinny look.
What role do carbohydrates play in building muscle?
Carbohydrates restore glycogen and recondition the muscles for performance and muscle growth.
Should I focus on consuming specific types of fats for muscle growth?
Yes! You should focus on eating monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats and avoid saturated and trans fats.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats increase your good cholesterol (healthy fats that keep your heart healthy), while trans fat builds your bad cholesterol, which sooner clogs the arteries and reduces blood flow to the heart, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Some trans fats include fries (deep fried fast food), cream, cookies, cakes, and other processed food.
How important is timing when it comes to eating for muscle growth?
Timing is important when it comes to muscle growth. A study showed that consuming nutrient-rich meals after exercise can enhance anabolic response and muscle protein net balance. This means you should eat after exercise.
While I agree about eating post-workout, I also recommend finding what works for you and adjust your meals to your training. Also, don’t eat if you are not hungry just because you “have to.”
Consume smaller meals every two to three hours, too. This can regulate your blood glucose and avoid crashes, but still fuel you and your muscles adequately.
Can I gain muscle without increasing my calorie intake?
You can gain muscle without increasing your calorie intake, but the result will be way slower and less visible. Other factors like your training style and intensity, genetics will also influence how visible your result will be on a calorie deficit or maintenance!
Calorie surplus is often required for best results!
What role do vitamins and minerals play in muscle growth, and how can I ensure I’m getting enough of them?
Vitamins and minerals are essential for protein synthesis, energy production, bone and muscle health.
To ensure you’re getting enough, maintain a healthy balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and dairy.
Can I gain muscle on a vegetarian or vegan diet?
It is possible to gain muscle on a vegetarian or vegan diet. As plant based sources are lower in protein then lean meat, you may require more supplements more frequently, like protein as well as bigger meal portions.
What are some good snacks to eat for muscle growth?
Vegetable sticks with hummus, chicken slices, turkey, ham, nuts, tuna, Greek yogurt, and protein shakes are all great snack options for muscle growth!
How can I create a meal plan that supports muscle growth?
First, calculate your required macronutrients. Once you know that, implement the 20 best foods to gain muscle and strength.
Alternatively you can ask the help of a nutritionist or a dietitian.